How to Fill or Write a Cheque Correctly: A Comprehensive Guide
April 15, 2025
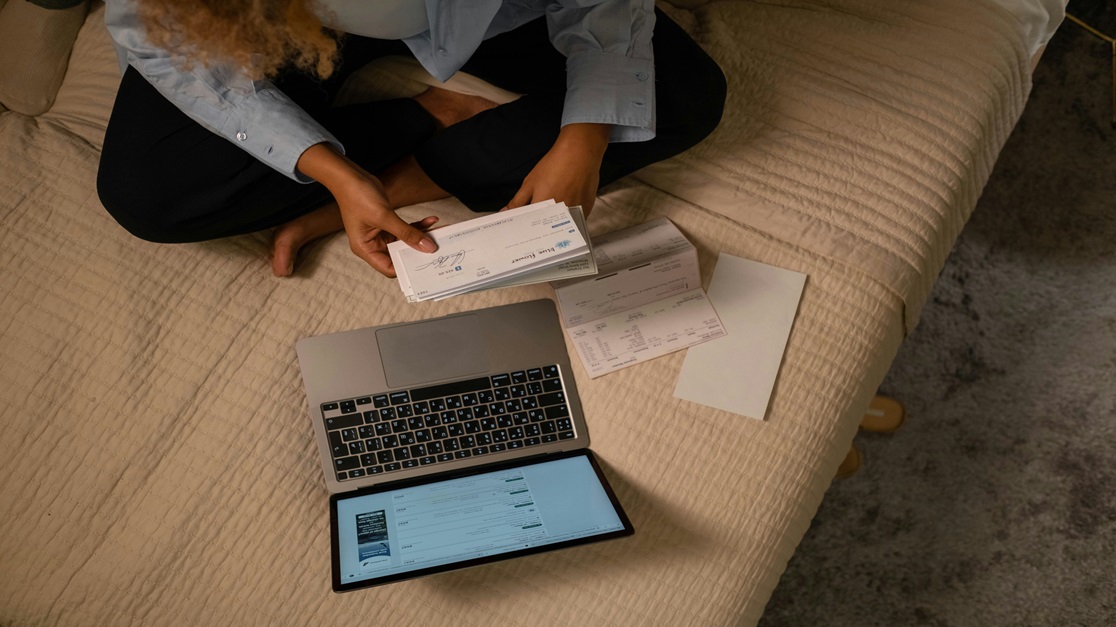

Cheques remain a significant mode of financial transactions in India, despite the rise of digital payments. Whether for personal or business use, knowing how to fill a cheque correctly is essential to prevent errors, fraud, or rejection. In this guide, we’ll walk you through the steps to fill a cheque properly, along with an overview of its types, advantages, disadvantages, and best practices.
Parts of a Cheque
Understanding the different sections of a cheque helps in filling it out accurately. Here are the key parts with examples:
- Date Field: Write the date in DD/MM/YYYY format. For example, if issuing a cheque on 5th February 2025, write it as 05/02/2025.
- Payee’s Name: Mention the name of the individual or entity receiving the payment. For instance, if paying ABC Enterprises, write “ABC Enterprises” without any spelling mistakes.
- Amount in Numbers: Enter the amount in digits, ensuring clarity and no overwriting. Example: Rs. 10,000/- should be written as "10000/-" without spaces.
- Amount in Words: Write the amount in words to avoid tampering. Example: “Ten thousand rupees only” and draw a line to prevent additions.
- Account Holder’s Signature: Sign the cheque at the bottom right corner using the signature registered with the bank.
- Cheque Number: A unique 6-digit number printed on the cheque for tracking, usually found at the bottom left.
- MICR Code: Found at the bottom, it is used for electronic processing and verification.
- IFSC Code: Helps in identifying the bank branch during electronic transactions and is printed near the MICR code.
Step-by-Step Guide to Filling a Cheque
- Write the Date: Use the current or post-dated cheque format to avoid misuse.
- Enter the Payee’s Name: Ensure correct spelling to avoid payment rejection.
- Mention the Amount in Numbers: E.g., Rs. 10,000/- (Avoid spaces between digits).
- Write the Amount in Words: E.g., “Ten thousand rupees only” and draw a line to prevent additions.
- Sign the Cheque: Use the same signature as recorded with the bank.
- Cross the Cheque (if required): For secure transactions, mark two parallel lines at the top left.
Different Types of Cheques
- Bearer Cheque: A Bearer Cheque is one where the person holding the cheque can encash it without additional verification. This type is risky as it can be encashed by anyone who has possession of it.
- Order Cheque: An Order Cheque is payable only to the individual or entity specified on the cheque. The payee needs to provide identity proof for verification before encashing the cheque.
- Crossed Cheque: A Crossed Cheque contains two parallel lines on the top left, indicating that the cheque amount can only be deposited into a bank account. This minimizes the risk of misuse and unauthorized encashment.
- Post-Dated Cheque: A Post-Dated Cheque is written with a future date, ensuring that the payee can encash it only on or after the specified date. It is commonly used for scheduled payments like loan EMIs and rent.
- Self Cheque: A Self Cheque is issued by the account holder when they need to withdraw cash for personal use. In this case, the payee field is written as “Self,” allowing the account holder to encash it at the bank.
Advantages of Using Cheques
- Secure Payment Method: Unlike cash, cheques leave a paper trail.
- Useful for Large Transactions: Ideal for business payments and loans.
- Post-Dated Payments: Enables scheduled payments.
- No Need for Cash Handling: Reduces the risk of theft or loss.
Disadvantages of Using Cheques
- Processing Time: Cheque clearance takes 1-3 working days.
- Risk of Dishonour: Insufficient funds may lead to cheque bounce penalties.
- Forgery and Fraud Risks: Signature mismatches or altered cheques can lead to losses.
- Not Ideal for Instant Payments: Unlike digital payments, cheques require manual clearance.
Best Practices for Using Cheques Safely
- Use a Permanent Ink Pen: Prevents alterations or tampering.
- Do Not Sign a Blank Cheque: Always fill in all details before signing.
- Keep Your Signature Consistent: Signature mismatches may lead to rejection.
- Issue Crossed Cheques When Possible: To reduce the risk of misuse.
- Maintain a Cheque Register: Keep a record of issued cheques.
Final Thoughts
Cheques continue to be a reliable method of financial transactions in India. While they offer security and convenience, proper usage is crucial to avoid fraud and transaction failures. By following the right steps and best practices, you can ensure seamless and secure cheque transactions.
Enjoy easy banking with Ujjivan Small Finance Bank. Save more with our high-interest Savings Account and Deposit products. Need cash for your business or personal needs? Apply for MSME Loans or Micro Loans with us – we offer competitive rates and quick disbursal. We also offer vehicle loans and home loans tailored for your unique requirements. Experience a smooth banking journey with Ujjivan SFB!
FAQs
1. Can I write a cheque with a pencil?
No, always use a pen to avoid alterations.
2. What happens if I sign differently than my bank records?
The cheque may be rejected due to a signature mismatch.
3. How long does it take to clear a cheque?
It usually takes 1-3 working days for a local cheque and up to 7 days for outstation cheques.
4. Can I cancel a cheque after issuing it?
Yes, you can request a stop payment from your bank before it is processed.
5. What should I do if I make a mistake while filling a cheque?
Cancel the cheque and issue a new one to avoid any misuse.
6. Is there a validity period for cheques in India?
Yes, cheques are valid for 3 months from the issue date.
7. What is a post-dated cheque, and how is it used?
A post-dated cheque is written for a future date and is often used for loan EMIs and rent payments.
8. Can I deposit a cheque in any bank?
Yes, but clearance time may vary if it is from a different bank.
9. What is a dishonoured cheque?
A cheque that is returned due to insufficient funds, incorrect details, or signature mismatch.
10. What is the difference between a bearer cheque and an order cheque?
A bearer cheque can be encashed by anyone holding it, while an order cheque is payable only to the specified person.
Latest Blogs

Telangana Housing Board & KPHB Colony: A Guide to Affordable Urban Housing in Hyderabad
March 14, 2025
As Telangana continues its rapid urbanisation journey, two key housing entities—Telangana Housing Board (THB) and Kukatpally Housing Board Colony (KPHB)—have played critical roles in shaping the state's real estate ecosystem.

Does Checking CIBIL Score Frequently Lower Your Credit Points?
April 07, 2025
Imagine you're planning to apply for a home loan, a credit card, or even a car loan. Naturally, you want to ensure your CIBIL score is in good shape before proceeding.

Explained: Can NRIs Buy an Agricultural Land in India?
April 03, 2025
Real estate investment is often a top priority for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) looking to retain strong financial ties to India.
How to Improve Your CIBIL Score from 600 to 750: A Step-by-Step Guide
April 02, 2025
Your CIBIL score is like your financial reputation—banks check it before approving loans or credit cards. If your score is hovering around 600, you might face difficulties in securing credit or may get loans with higher interest rates.

What Happens When You Leave Your Savings Account Unused?
April 01, 2025
Imagine waking up one day to find that your hard-earned money is locked away and inaccessible. Sounds stressful, right? This is precisely what happens when you leave your Savings Account inactive for too long.





